# 1、自行设计一个反射的实例,说明 class 对象的使用方法
项目代码:ReflectionTest
Java 中的反射是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;并且能改变它的属性。
首先创建两个测试类,学生类 Student 和教师类 Teacher,重载他们的 toString 函数便于显示信息。
package dao; | |
public class Student { | |
private String name; // 姓名 | |
private long stuNum; // 学号 | |
private int age; // 年龄 | |
private String profession; // 专业班级 | |
private double grade; // 课程成绩 | |
public Student() { | |
name = null; | |
grade = 0; | |
} | |
public Student(String name, long stuNum, int age, String profession, double grade) { | |
this.name = name; | |
this.stuNum = stuNum; | |
this.age = age; | |
this.profession = profession; | |
this.grade = grade; | |
} | |
public void setStudent(String name, double grade) { | |
this.name = name; | |
this.grade = grade; | |
} | |
public String getName() {return name;} | |
public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;} | |
public long getStuNum() {return stuNum;} | |
public void setStuNum(long stuNum) {this.stuNum = stuNum;} | |
public int getAge() {return age;} | |
public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;} | |
public String getProfession() {return profession;} | |
public void setProfession(String profession) {this.profession = profession;} | |
public double getGrade() {return grade;} | |
public void setGrade(double g) {this.grade = g;} | |
@Override | |
public String toString() { | |
return "Student{" + | |
"name='" + name + '\'' + | |
", stuNum=" + stuNum + | |
", age=" + age + | |
", profession='" + profession + '\'' + | |
", grade=" + grade + | |
'}'; | |
} | |
} |
教师类 Teacher
package dao; | |
public class Teacher { | |
private String name; // 姓名 | |
private int age; // 年龄 | |
private String prof; // 教哪个系 | |
private String course; // 所教课程 | |
private double salary; // 每月工资 | |
public Teacher() {} | |
public Teacher(String name, int age, String prof, String course, double salary) { | |
this.name = name; | |
this.age = age; | |
this.prof = prof; | |
this.course = course; | |
this.salary = salary; | |
} | |
// getter & setter 可略 | |
public String getName() {return name;} | |
public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;} | |
public int getAge() {return age;} | |
public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;} | |
public String getProf() {return prof;} | |
public void setProf(String prof) {this.prof = prof;} | |
public String getCourse() {return course;} | |
public void setCourse(String course) {this.course = course;} | |
public double getSalary() {return salary;} | |
public void setSalary(double salary) {this.salary = salary;} | |
@Override | |
public String toString() { | |
return "Teacher{" + | |
"name='" + name + '\'' + | |
", age=" + age + | |
", prof='" + prof + '\'' + | |
", course='" + course + '\'' + | |
", salary=" + salary + | |
'}'; | |
} | |
} |
通过 Class 类我们就可以在程序中动态地获取成员变量、成员方法、接口、超类、构造方法等,每一个类在 JVM 中有且仅有一个 Class 实例
查阅 API 可以看到 Class 有很多方法:
- getName ():获得类的完整名字。
- getFields ():获得类的 public 类型的属性。
- getDeclaredFields ():获得类的所有属性。包括 private 声明的和继承类
- getMethods ():获得类的 public 类型的方法。
- getDeclaredMethods ():获得类的所有方法。包括 private 声明的和继承类
- getMethod (String name, Class [] parameterTypes):获得类的特定方法,name 参数指定方法的名字,parameterTypes 参数指定方法的参数类型。
- getConstructors ():获得类的 public 类型的构造方法。
- getConstructor (Class [] parameterTypes):获得类的特定构造方法,parameterTypes 参数指定构造方法的参数类型。
- newInstance ():通过类的不带参数的构造方法创建这个类的一个对象。
下面是测试函数
import dao.Student; | |
import dao.Teacher; | |
import java.lang.reflect.*; | |
public class Main { | |
public static void printClassInfo(Object object) { | |
Class c = object.getClass(); | |
System.out.println("Name: " + c.getName()); | |
System.out.println("------------Fields----------"); | |
Field[] fields = c.getDeclaredFields(); // 获得类声明的所有字段 包括私有的(如果只有 getFields 的话是没有私有字段的) | |
for(Field field : fields) { | |
System.out.println("FieldName: " + field.getName()); | |
} | |
System.out.println("------------Methods----------"); | |
Method[] methods = c.getMethods(); // 获得类的所有方法 | |
for(Method method : methods) { | |
System.out.println("Method: " + method.getName()); | |
} | |
} | |
public static void main(String[] args) { | |
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("王老师", 30, "计算机科学与技术", "计算机导论", 7000); | |
Student student = new Student("李明", 201916012, 19, "计科F1901", 92); | |
System.out.println( teacher.toString() ); | |
System.out.println( student.toString() ); | |
printClassInfo(teacher); | |
System.out.println(); | |
printClassInfo(student); | |
} | |
} |
可以看到输出结果如图:


# 2、自行设计一个实例,说明 Collection 接口和迭代器,比较器的使用方法
Collection 集合是 java 中提供的一种容器,可以用来存储多个数据,这里以单列集合 java.util.Collection 为例。Collection 是所有单列集合(如 List)的父接口,因此在 Collection 中定义了单列集合 (List 和 Set) 通用的一些方法,这些方法可用于操作所有的单列集合。方法如下:
- public boolean add (Obeject o): 把给定的对象添加到当前集合中 。
- public void clear () : 清空集合中所有的元素。
- public boolean remove (Obeject o): 把给定的对象在当前集合中删除。
- public boolean contains (Obeject o): 判断当前集合中是否包含给定的对象。
- public boolean isEmpty (): 判断当前集合是否为空。
- public int size (): 返回集合中元素的个数。
- public Object [] toArray (): 把集合中的元素,存储到数组中。
迭代器:在程序开发中,经常需要遍历集合中的所有元素。针对这种需求,JDK 专门提供了一个接口 java.util.Iterator。Iterator 接口主要用于迭代访问(即遍历)Collection 中的元素,因此 Iterator 对象也被称为迭代器。public Iterator iterator (): 获取集合对应的迭代器,用来遍历集合中的元素。这个概念与 c++ 中 STL 的 iterator 一致(
Iterator 接口的常用方法如下:
- public Obeject next (): 返回迭代的下一个元素。
- public boolean hasNext (): 如果仍有元素可以迭代,则返回 true。
比较器:
指的是集合存储的元素的特性,如果元素是可比较的则可以进行相应的排序,否则不行。对于 Comparable 接口来说,它往往是进行比较类需要实现的接口,它仅包含一个有 compareTo () 方法,只有一个参数,返回值为 int,返回值大于 0 表示对象大于参数对象;小于 0 表示对象小于参数对象;等于 0 表示两者相等
import java.util.*; | |
public class Main { | |
public static <T> void printAll(Collection<T> collection) { | |
Iterator<T> it = collection.iterator(); | |
while(it.hasNext()) { | |
T nowT = it.next(); | |
System.out.println(nowT); | |
} | |
} | |
public static void main(String[] args) { | |
ArrayList<String> col = new ArrayList<String>(); | |
col.add("abcs"); | |
col.add("bdfs"); | |
Collections.addAll(col, "test1", "test4", "test2","csnw"); | |
// 采用迭代器 显示所有 Collection 元素 | |
printAll(col); | |
System.out.println("\n字典序升序排一下~"); | |
Collections.sort(col, new Comparator<String>() { | |
@Override | |
public int compare(String s1, String s2) { | |
return s1.compareTo(s2); | |
} | |
}); | |
printAll(col); | |
System.out.println("\n字典序降序排一下~"); | |
Collections.sort(col, new Comparator<String>() { | |
@Override | |
public int compare(String s1, String s2) { | |
return s2.compareTo(s1); | |
} | |
}); | |
printAll(col); | |
} | |
} |
输出如图所示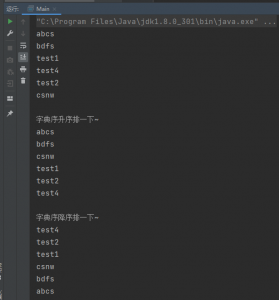
# 3、比较 JavaScript,Python 和 Java 使用正则表达式的异同
使用 Python 的正则时,字符串前面加上‘r’,告诉编译器这个 string 是个 raw string,不要转义 ‘’ 。 例如,\n 在 raw string 中,是两个字符,\ 和 n, 而不会转意为换行符。由于正则表达式和 \ 会有冲突,因此,当一个字符串使用了正则表达式后,最好在前面加上’r’。
javascript 中的正则表达式和 java 的正则表达式基本上是相同的,区别在于分组引用和对象,方法以及 Java 的正则比 js 的多一个转义符号 “\”
更具体的异同看这篇博客:正则表达式:JavaScript、Java、Python 基础语法
4、自学工厂设计模式、观察者模式并写出相应的例程。
懒得写废话 了()扒拉了两篇博客
设计模式之工厂模式(factory pattern)
JAVA 设计模式之观察者模式