题目集总目录
学习指路博客 二叉搜索树与平衡二叉树
# 04 - 树 4 是否同一棵二叉搜索树 (25 分)
本题链接
小白专场将详细介绍 C 语言实现方法,属于基本训练,一定要做
# 题目大意
对于输入的各种插入序列,判断它们是否能生成一样的二叉搜索树。
# 思路
1. 分别建两棵树的判别方法
2. 不建树直接判断序列
3. 建一棵树再判别其他序列是否与该树一致
这里采用的是思路 3
# 代码
#include <iostream> | |
using namespace std; | |
#define maxsize 11 | |
typedef struct TNode* Tree; | |
struct TNode { | |
int data; | |
Tree left,right; | |
int flag; // 判断是否访问过 | |
}; | |
void Clear(Tree R) { // 清除标记 | |
if(!R) return; | |
R->flag = 0; | |
Clear(R->left); | |
Clear(R->right); | |
} | |
void FreeTree(Tree R) { // 清空该树 | |
if(!R) return; | |
FreeTree(R->left); | |
FreeTree(R->right); | |
delete R; | |
} | |
Tree NewNode(int data) {// | |
Tree R = new TNode; | |
R->data = data; | |
R->left = R->right = NULL; | |
R->flag = 0; | |
return R; | |
} | |
Tree BST_Insert(int data, Tree R) { | |
if (!R) R = NewNode(data); | |
else { | |
if(data > R->data) // 大于该结点,插入到右子树 | |
R->right = BST_Insert(data, R->right); | |
else // 小于或等于该结点,插入到左子树 | |
R->left = BST_Insert(data, R->left); | |
} | |
return R; | |
} | |
Tree Build(int N) { | |
Tree R = NULL; | |
int x; | |
cin >> x; | |
R = NewNode(x); | |
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i) { | |
cin >> x; | |
R = BST_Insert(x, R); | |
} | |
return R; | |
} | |
bool check(int data, Tree R) { | |
if(R->flag) {// 已经访问过了 | |
if(data < R->data) | |
return check(data, R->left); | |
else if(data > R->data) | |
return check(data, R->right); | |
else return false; | |
} else { | |
if(data == R->data) { | |
R->flag = 1; | |
return true; | |
} else return false; | |
} | |
} | |
bool judge(Tree R1, int N) { | |
int x; | |
bool flag = true; | |
if(N && R1) { | |
cin >> x; | |
if(x != R1->data) flag = false; | |
R1->flag = 1; | |
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i) { | |
cin >> x; | |
if(flag && (!check(x,R1))) flag = false; | |
} | |
} | |
return flag; | |
} | |
int main() { | |
int N, L; | |
cin >> N; | |
while(N) { | |
cin >> L; | |
Tree R1; | |
R1 = Build(N); | |
for(int i = 0; i < L; ++i) { | |
if(judge(R1, N)) | |
cout << "Yes" << endl; | |
else cout << "No" << endl; | |
Clear(R1); // 清除标记 | |
} | |
FreeTree(R1); | |
cin >> N; | |
} | |
return 0; | |
} |
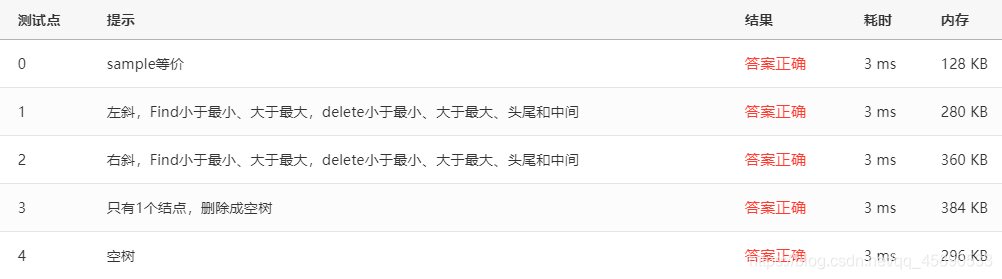
# 测试点
测试点如下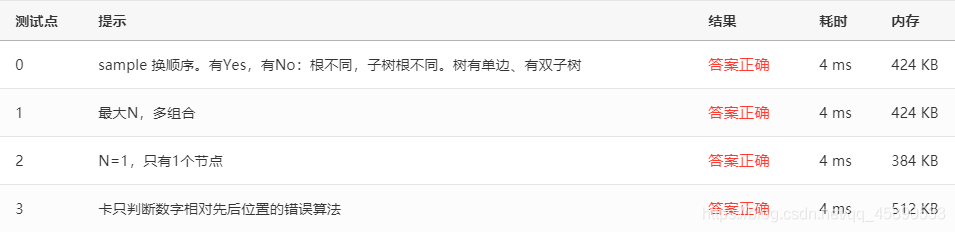
# 04 - 树 5 Root of AVL Tree (25 分)
本题链接
2013 年浙江大学计算机学院免试研究生上机考试真题,是关于 AVL 树的基本训练,一定要做
# 题目大意
现在给定一插入序列,输出生成的 AVL 树的根。
# 代码
#include <iostream> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
using namespace std; | |
#define maxsize 11 | |
typedef struct AVLNode* AVLTree; | |
struct AVLNode { | |
int data; | |
AVLTree left,right; | |
int Height; | |
}; | |
void FreeTree(AVLTree R) { // 清空该树 | |
if(!R) return; | |
FreeTree(R->left); | |
FreeTree(R->right); | |
delete R; | |
} | |
int GetHeight(AVLTree R) { | |
if(R) | |
return R->Height; | |
else | |
return 0; | |
} | |
AVLTree SingleLeftRotate(AVLTree R) { //LL 单旋 | |
AVLTree RL = R->left; | |
R->left = RL->right; | |
RL->right = R; | |
R->Height = max( GetHeight(R->left), GetHeight(R->right) ) + 1; | |
RL->Height = max( GetHeight(RL->left), R->Height) + 1; | |
return RL; | |
} | |
AVLTree SingleRightRotate(AVLTree R) { //RR 单旋 | |
AVLTree RR = R->right; | |
R->right = RR->left; | |
RR->left = R; | |
R->Height = max( GetHeight(R->left), GetHeight(R->right) ) + 1; | |
RR->Height = max( R->Height, GetHeight(RR->right) ) + 1; | |
return RR; | |
} | |
AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotate(AVLTree R) { //LR 旋转 | |
R->left = SingleRightRotate(R->left); | |
return SingleLeftRotate(R); | |
} | |
AVLTree DoubleRightLeftRotate(AVLTree R) { //RL 旋转 | |
R->right = SingleLeftRotate(R->right); | |
return SingleRightRotate(R); | |
} | |
AVLTree NewNode(int data) {// | |
AVLTree R = new AVLNode; | |
R->data = data; | |
R->left = R->right = NULL; | |
R->Height = 0; | |
return R; | |
} | |
AVLTree AVL_Insert(int data, AVLTree R) { | |
if (!R) R = NewNode(data); | |
else if(data < R->data) { // 插入到左子树 | |
R->left = AVL_Insert(data, R->left); | |
if(GetHeight(R->left) - GetHeight(R->right) == 2) { // 需要左旋 | |
if (data < R->left->data) | |
R = SingleLeftRotate(R); // 需要左单旋 | |
else | |
R = DoubleLeftRightRotate(R);// 左 - 右双旋 | |
} | |
} else if(data > R->data) { // 插入到右子树 | |
R->right = AVL_Insert(data, R->right); | |
if(GetHeight(R->left) - GetHeight(R->right) == -2) { // 需要右旋 | |
if (data > R->right->data) | |
R = SingleRightRotate(R); // 需要右单旋 | |
else | |
R = DoubleRightLeftRotate(R);// 右 - 左双旋 | |
} | |
} | |
R->Height = max(GetHeight(R->left), GetHeight(R->right)) + 1; | |
return R; | |
} | |
AVLTree Build(int N) { | |
AVLTree R = NULL; | |
int x; | |
cin >> x; | |
R = NewNode(x); | |
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i) { | |
cin >> x; | |
R = AVL_Insert(x, R); | |
} | |
return R; | |
} | |
int main() { | |
int N, L; | |
AVLTree R; | |
cin >> N; | |
R = Build(N); | |
cout << R->data << endl; | |
return 0; | |
} |
# 测试点
测试点如下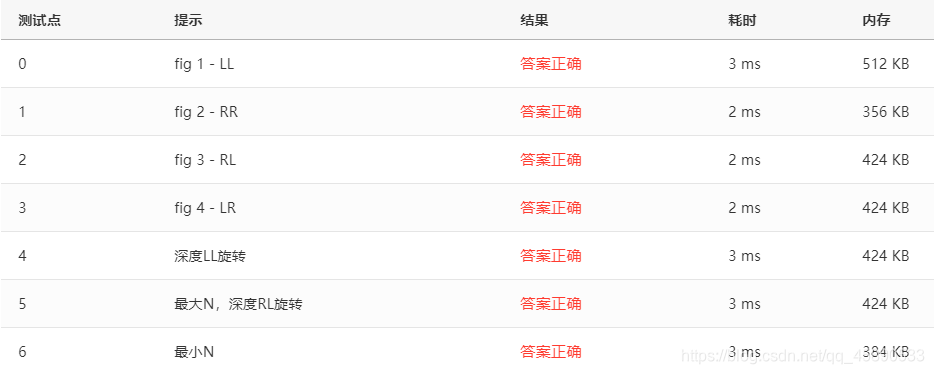
# 04 - 树 6 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分)
本题链接
2013 年秋季 PAT 甲级真题,略有难度,量力而行。第 7 周将给出讲解。
# 题目大意
现在给定一完全二叉搜索树的插入序列,输出生成的完全二叉树的层次遍历序列
# 思路
因为是完全二叉搜索树,由左子树结点值 > 根结点结点值 > 右子树结点值这个性质,可将给定输入序列从小到大排好序后即为该树的中序遍历序列,然后根据中序遍历的结果递归构造层次遍历序列。
中序遍历序列中,总结点数为 n 时,若左子树的节点数为 x 的,则根节点即为第 x+1 个元素。而如何知道左子树的结点树呢,这也是由完全二叉树的性质决定的,因为 n 个节点的完全二叉树,它的左子树结点数是确定的,则可以设置一个根据总结点数求左子树结点树的函数。可用到二叉树以下几个性质:
- n 个结点的二叉树,其深度为 log2(n) + 1
- 二叉树的第 i 层,最多有 2i-1 个结点
- 深度为 k 的二叉树,最多有 2k-1 个结点
# 代码
#include <iostream> | |
#include <cmath> | |
#include <algorithm> | |
using namespace std; | |
#define maxsize 2002 | |
#define Null -1 | |
int a[maxsize],b[maxsize];// 中序遍历的结果 层次遍历的结果 | |
int GetLeftSum(int n) { // 获取左子树总结点数 n 为结点总数 | |
if(n == 1) return 0; | |
int h = log2(n);// 除最后一层的深度 | |
int Lsum = pow(2, h-1) - 1; // 除最后一层之外的左子树结点个数 | |
// 即为 (2^h-1-1)/2 | |
int last = n - (pow(2, h) - 1); // 最后一层结点数 | |
if(last <= pow(2, h-1)) | |
Lsum += last; | |
else Lsum += pow(2, h-1); | |
return Lsum; | |
} | |
void LevelOrderRebuild(int left, int right,int bR) { | |
int n = right - left + 1;// 总结点数 | |
if(n == 0) return; | |
int leftlen = GetLeftSum(n); | |
int aR = left + leftlen; | |
b[bR] = a[aR]; | |
int nl = bR * 2 + 1; | |
int nr = nl + 1; | |
LevelOrderRebuild(left, aR-1, nl); | |
LevelOrderRebuild(aR+1, right, nr); | |
} | |
int main() { | |
int N; | |
cin >> N; | |
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) | |
cin >> a[i]; | |
sort(a, a+N); | |
LevelOrderRebuild(0, N-1, 0); | |
for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { | |
if(i) { | |
cout << " " << b[i]; | |
} else cout << b[i]; | |
} | |
return 0; | |
} |
# 测试点
测试点如下: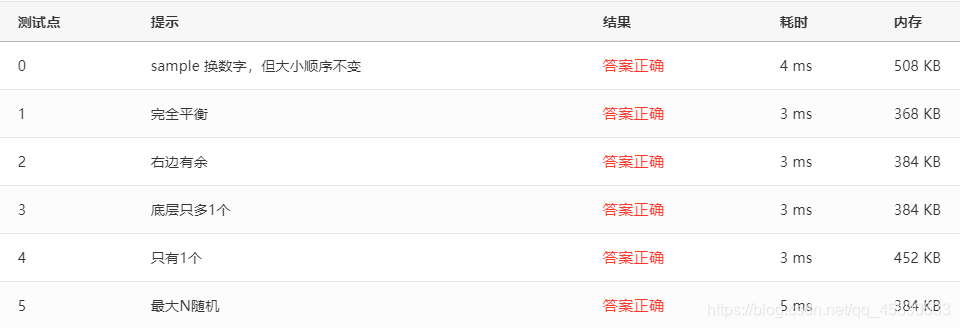
# 04 - 树 7 二叉搜索树的操作集 (30 分)
本题链接
# 题目大意
二叉搜索树的操作集实现
# 代码
#include <stdio.h> | |
#include <stdlib.h> | |
typedef int ElementType; | |
typedef struct TNode *Position; | |
typedef Position BinTree; | |
struct TNode{ | |
ElementType Data; | |
BinTree Left; | |
BinTree Right; | |
}; | |
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT ) { /* 先序遍历,由裁判实现,细节不表 */ | |
if(BT) { | |
printf("%d", BT->Data); | |
PreorderTraversal( BT->Left); | |
PreorderTraversal( BT->Right); | |
} | |
} | |
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT ) { /* 中序遍历,由裁判实现,细节不表 */ | |
if(BT) { | |
InorderTraversal( BT->Left); | |
printf("%d", BT->Data); | |
InorderTraversal( BT->Right); | |
} | |
} | |
BinTree Insert( BinTree BST, ElementType X ); | |
BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X ); | |
Position Find( BinTree BST, ElementType X ); | |
Position FindMin( BinTree BST ); | |
Position FindMax( BinTree BST ); | |
int main() | |
{ | |
BinTree BST, MinP, MaxP, Tmp; | |
ElementType X; | |
int N, i; | |
BST = NULL; | |
scanf("%d", &N); | |
for ( i=0; i<N; i++ ) { | |
scanf("%d", &X); | |
BST = Insert(BST, X); | |
} | |
printf("Preorder:"); PreorderTraversal(BST); printf("\n"); | |
MinP = FindMin(BST); | |
MaxP = FindMax(BST); | |
scanf("%d", &N); | |
for( i=0; i<N; i++ ) { | |
scanf("%d", &X); | |
Tmp = Find(BST, X); | |
if (Tmp == NULL) printf("%d is not found\n", X); | |
else { | |
printf("%d is found\n", Tmp->Data); | |
if (Tmp==MinP) printf("%d is the smallest key\n", Tmp->Data); | |
if (Tmp==MaxP) printf("%d is the largest key\n", Tmp->Data); | |
} | |
} | |
scanf("%d", &N); | |
for( i=0; i<N; i++ ) { | |
scanf("%d", &X); | |
BST = Delete(BST, X); | |
} | |
printf("Inorder:"); InorderTraversal(BST); printf("\n"); | |
return 0; | |
} | |
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */ | |
BinTree Insert( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) { | |
if(!BST) { | |
BST = (BinTree) malloc(sizeof(struct TNode)); | |
BST->Data = X; | |
BST->Left = BST->Right = NULL; | |
return BST; | |
} else { | |
if(X < BST->Data) | |
BST->Left = Insert(BST->Left, X); | |
else if(X > BST->Data) | |
BST->Right = Insert(BST->Right, X); | |
} | |
return BST; | |
} | |
BinTree Delete( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) { | |
Position tmp; | |
if(!BST) printf("Not Found\n"); | |
else if (X < BST->Data) | |
BST->Left = Delete(BST->Left, X); | |
else if (X > BST->Data) | |
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right, X); | |
else { // 找到了要删除的结点 | |
if (BST->Left && BST->Right) { // 待删除结点有左右两个孩子 | |
tmp = FindMin(BST->Right); // 在右子树中找最小的元素填充删除节点 | |
BST->Data = tmp->Data; | |
BST->Right = Delete(BST->Right, tmp->Data); | |
// 填充完后,在右子树中删除该最小元素 | |
} | |
else { // 待删除结点有 1 个或无子结点 | |
tmp = BST; | |
if (!BST->Left) // 有有孩子或无子节点 | |
BST = BST->Right; | |
else if (!BST->Right) | |
BST = BST->Left; | |
free(tmp); | |
} | |
} | |
return BST; | |
} | |
Position Find( BinTree BST, ElementType X ) { | |
while (BST) { | |
if(X < BST->Data) | |
BST = BST->Left; | |
else if(X > BST->Data) | |
BST = BST->Right; | |
else return BST; | |
} | |
return NULL; | |
} | |
Position FindMin( BinTree BST ) { | |
if(BST) { | |
while(BST->Left) | |
BST = BST->Left; | |
} | |
return BST; | |
} | |
Position FindMax( BinTree BST ) { | |
if(BST) { | |
while(BST->Right) | |
BST = BST->Right; | |
} | |
return BST; | |
} |
# 测试点
测试点如下